React:三目並べ(履歴の保持)
参考:タイムトラベルの追加
最後の演習として、ゲームを過去の手番に「巻き戻す」ことができるようにしましょう。
stateをまたリフトアップ
SquaresからBoardにstateを移動したように、BoardからGamesにstateを移動します。
- xIsNextはXかOの切り替え管理、historyは履歴を管理するstate変数
- BoardコンポーネントにxIsNext、currentSquares、イベントハンドラ関数のhandlePlayをpropsで受け渡し
export default function Game() {
const [xIsNext, setXIsNext] = useState(true);
const [history, setHistory] = useState([Array(9).fill(null)]);
const currentSquares = history[history.length - 1];
function handlePlay(nextSquares) {
setHistory([...history, nextSquares]);
setXIsNext(!xIsNext);
}
return (
<div className="game">
<div className="game-board">
<Board xIsNext={xIsNext} squares={currentSquares} onPlay={handlePlay} />
</div>
<div className="game-info">
<ol></ol>
</div>
</div>
)
}Boardの変更
メインコンポーネントBoardがやっていたことをGamesに引き継ぐため、重複箇所を削除します。
- Gamesからpropを受け取る
- マス目の状態保持とXかOの状態を保持していた二つのstate変数を削除
- setSquares(マス目の状態を更新)とsetXIsNext(XかOか更新)をonPlay(nextSquares)に変更
function Board({xIsNext, squares, onPlay}) {
function handleClick(i) {
if (squares[i] || calculateWinner(squares)) {
return;
}
const nextSquares = squares.slice();
console.log('nextSquares', nextSquares);
if (xIsNext) {
nextSquares[i] = "X";
} else {
nextSquares[i] = "O";
}
onPlay(nextSquares);
}
..historyとはここで、
[...history, nextSquares]というコードは、historyのすべての要素の後にnextSquaresが繋がった新しい配列を作成します。(この...historyはスプレッド構文であり、「historyのすべての項目をここに列挙せよ」のように読みます。)例えば、
historyが[[null,null,null], ["X",null,null]]でnextSquaresが["X",null,"O"]の場合、新しい[...history, nextSquares]配列は[[null,null,null], ["X",null,null], ["X",null,"O"]]になります。
ここまでで、ゲームの履歴を記録しつつ、state移動する前と変わらない操作ができます。
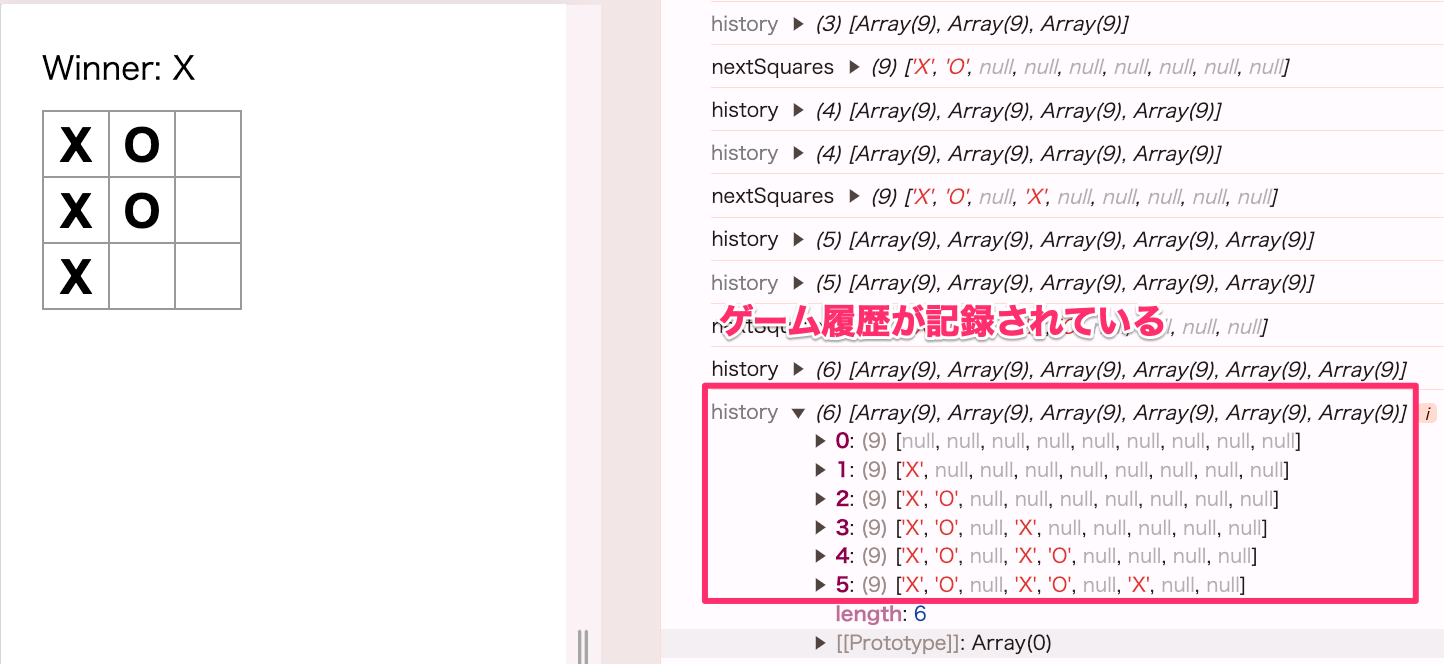
ゲームの履歴を表示する
メインコンポーネントGameに追記します。
function jumpTo(nextMove) {
}
const moves = history.map((squares, move) => {
let description;
if(move > 0) {
description = 'Go to move #' + move;
} else {
description = 'Go to game start'
}
return (
<li>
<button onClick={() => jumpTo(move)}>{description}</button>
</li>
)
})
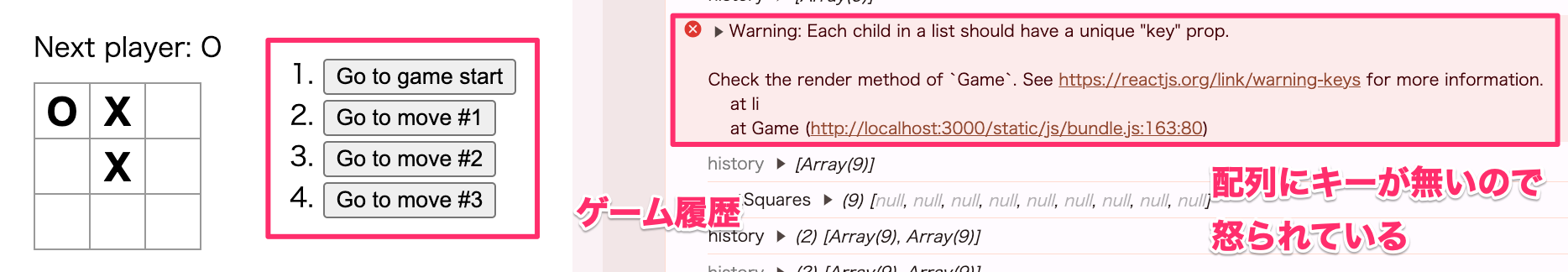
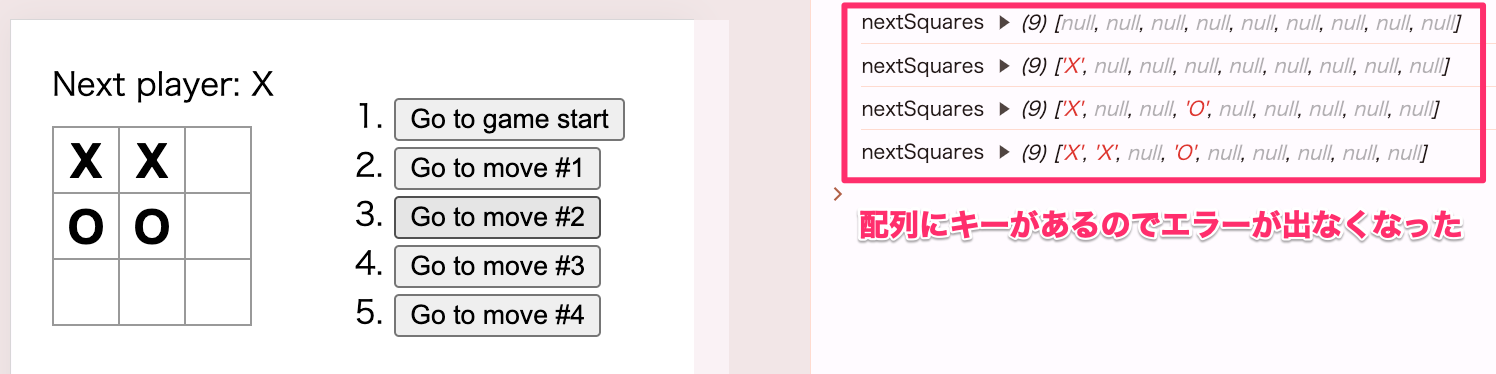
キーを追加してエラー解消
key はグローバルに一意である必要はなく、コンポーネントとその兄弟間で一意であれば十分です。
return (
<li key={move}>
<button onClick={() => jumpTo(move)}>{description}</button>
</li>
)
飛ぶための実装
現在ユーザが見ているのが何番目の着手であるのかを管理するための新しいstate変数「currentMove」を追加します。
export default function Game() {
const [xIsNext, setXIsNext] = useState(true);
const [history, setHistory] = useState([Array(9).fill(null)]);
const [currentMove, setCurrentMove] = useState(0);
const currentSquares = history[history.length - 1];ジャンプする関数「jumpTo」を用意します。nextMoveには管理番号が入っています。
「nextMove % 2 === 0」では、飛ぶ先の管理番号が偶数(=X)かどうかを判定してます。
偶数の場合trueとなり、Xを表示できるようになります。
function jumpTo(nextMove) {
setCurrentMove(nextMove);
setXIsNext(nextMove % 2 === 0);
}履歴更新機能の実装
巻き戻した時、不要な履歴を消すため「handlePlay」関数の実装をします。
before
function handlePlay(nextSquares) {
setHistory([...history, nextSquares]);
setXIsNext(!xIsNext);
}after
function handlePlay(nextSquares) {
const nextHistory = [...history.slice(0, currentMove + 1), nextSquares];
setHistory(nextHistory);
setCurrentMove(nextHistory.length - 1);
setXIsNext(!xIsNext);
}Game関数の更新
常に最後の着手をレンダーする代わりに、現在選択されている着手をレンダーするようにします:
export default function Game() {
...
const currentSquares = history[history.length - 1];after
export default function Game() {
...
const currentSquares = history[currentMove];
重複しているロジックをまとめる
XかOの判定に、「管理番号が偶数/奇数」「XIsNextがtrue/false」という2つの判定方法があります。これを管理番号(crrentMove)の偶数/奇数だけで判定するようにします。
before
export default function Game() {
...
const [xIsNext, setXIsNext] = useState(true);
function handlePlay(nextSquares) {
const nextHistory = [...history.slice(0, currentMove + 1), nextSquares];
setHistory(nextHistory);
setCurrentMove(nextHistory.length - 1);
setXIsNext(!xIsNext);
}
function jumpTo(nextMove) {
setCurrentMove(nextMove);
setXIsNext(nextMove % 2 === 0);
}after
export default function Game() {
...
const xIsNext = currentMove % 2 === 0;
function handlePlay(nextSquares) {
const nextHistory = [...history.slice(0, currentMove + 1), nextSquares];
setHistory(nextHistory);
setCurrentMove(nextHistory.length - 1);
}
function jumpTo(nextMove) {
setCurrentMove(nextMove);
}三目並べ終わり
全体のコード
import { useState } from "react";
function Square({value, onSquareClick}) {
return (
<button className="square" onClick={onSquareClick}>
{value}
</button>
);
}
function Board({xIsNext, squares, onPlay}) {
function handleClick(i) {
if (squares[i] || calculateWinner(squares)) {
return;
}
const nextSquares = squares.slice();
console.log('nextSquares', nextSquares);
if (xIsNext) {
nextSquares[i] = "X";
} else {
nextSquares[i] = "O";
}
onPlay(nextSquares);
}
const winner = calculateWinner(squares);
let status;
if (winner) {
status = "Winner: " + winner;
} else {
status = "Next player: " + (xIsNext ? "X" : "O");
}
return (
<>
<div className="status">{status}</div>
<div className="board-row">
<Square value={squares[0]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(0)}/>
<Square value={squares[1]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(1)}/>
<Square value={squares[2]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(2)}/>
</div>
<div className="board-row">
<Square value={squares[3]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(3)}/>
<Square value={squares[4]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(4)}/>
<Square value={squares[5]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(5)}/>
</div>
<div className="board-row">
<Square value={squares[6]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(6)}/>
<Square value={squares[7]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(7)}/>
<Square value={squares[8]} onSquareClick={() => handleClick(8)}/>
</div>
</>
);
}
export default function Game() {
const [history, setHistory] = useState([Array(9).fill(null)]);
const [currentMove, setCurrentMove] = useState(0);
const xIsNext = currentMove % 2 === 0;
const currentSquares = history[currentMove];
function handlePlay(nextSquares) {
const nextHistory = [...history.slice(0, currentMove + 1), nextSquares];
setHistory(nextHistory);
setCurrentMove(nextHistory.length - 1);
}
function jumpTo(nextMove) {
setCurrentMove(nextMove);
}
const moves = history.map((squares, move) => {
let description;
if(move > 0) {
description = 'Go to move #' + move;
} else {
description = 'Go to game start'
}
return (
<li key={move}>
<button onClick={() => jumpTo(move)}>{description}</button>
</li>
)
})
return (
<div className="game">
<div className="game-board">
<Board xIsNext={xIsNext} squares={currentSquares} onPlay={handlePlay} />
</div>
<div className="game-info">
<ol>{moves}</ol>
</div>
</div>
)
}
function calculateWinner(squares) {
const lines = [
[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 3, 6],
[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[0, 4, 8],
[2, 4, 6]
];
for (let i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) {
const [a, b, c] = lines[i];
if (squares[a] && squares[a] === squares[b] && squares[a] === squares[c]) {
return squares[a];
}
}
return null;
}
おめでとうございます! 以下のような機能を持つ三目並べのゲームが作成できました。
- 三目並べをプレイできる
- プレーヤがゲームに勝ったときにそれを判定して表示する
- ゲームの進行に伴って履歴を保存する
- プレーヤがゲームの履歴を振り返り、盤面の以前のバージョンを確認できる
よくできました! これで、React の仕組みについてかなりの理解が得られたことを願っています。
